OSAKA, Japan — Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd. (hereinafter “Nippon Shokubai”) has developed a new separator for alkaline water electrolysis by applying its unique organic-inorganic hybrid technology and sheet forming technology.
The new separator is suitable for producing “green hydrogen” because it has a high level of resistance against gas cross-permeation and high efficiency of hydrogen generation. Also, it can be handled easily even in the dry condition. The new separator assists the spread of “green hydrogen” worldwide and contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
To prevent global warming, many projects to reduce the emission of carbon dioxide gas have been carried out throughout the world. As part of these activities, fuel cells have begun to be used for various applications such as vehicles, and micro combined heat and power systems.
Today, the most common process of industrially generating hydrogen is the steam reforming process. However, this process has the problem of emitting carbon dioxide because it uses fossil-originated gas as a resource. Therefore, alkaline water electrolysis (Figure 1) using renewable energy is drawing worldwide attention as a means of hydrogen supply since it has no carbon dioxide emission. Also, large-scale demonstration projects are being promoted around the world.
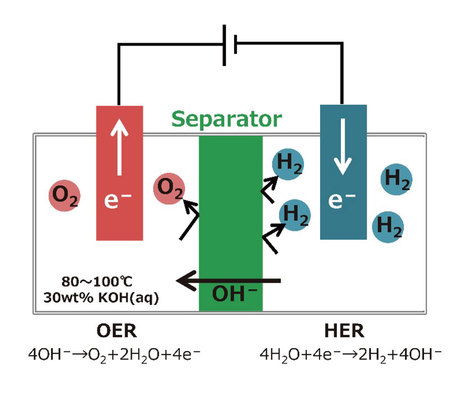
Fig. 1: Schematic diagram of alkaline water electrolysis
In this alkaline water electrolysis system, one of the key materials that affect the hydrogen production efficiency is the separator (green part in Fig. 1). A separator for alkaline water electrolysis requires high resistance against cross permeation of hydrogen and oxygen and low ohmic resistance of separators (high ionic conductivity). Moreover, as alkaline water electrolysis is operated in a very severe condition, like high-temperature and high-alkaline concentration, very few separators could be applied for alkaline water electrolysis.

Nippon Shokubai’s newly developed separator
Nippon Shokubai has successfully developed the new separator with high resistance against cross permeation of hydrogen and oxygen, and low ohmic resistance of separators (high ionic conductivity) for alkaline water electrolysis by applying its unique organic-inorganic hybrid technology and sheet-forming technology.
The company’s new separator can be expected to reduce electrical power consumption and enables higher hydrogen purity. It will introduce and exhibit this new separator at a Nippon Shokubai booth at the “the 11th International Rechargeable Battery Exhibition” to be held at Aomi Hall, Tokyo Big Sight, from February 26 (Wed.) to 28 (Fri.).
Read the most up to date Fuel Cell and Hydrogen Industry news at FuelCellsWorks




