Due to utilizing large amount of fossil fuels in modern industry, the eco-environmental problems and energy crises have attracted tremendous attention of human beings. Therefore, it has become a promising strategy to decrease exhaust emission by using solar energy instead of fossil fuels, because the former is a clean, safe and inexhaustible energy resource. Hydrogen (H2) is considered as one of the most promising energy sources to address the global energy crisis owing to the high energy density and free of carbon emission. Therefore, numerous methods, such as traditional thermalchemistry, electrocatalysis, photocatalysis and photoelectrocatalysis, have been utilized to produce H2. Among them, the technology for converting solar energy to H2 have been considered as the one of the greenest and sustainable technology.
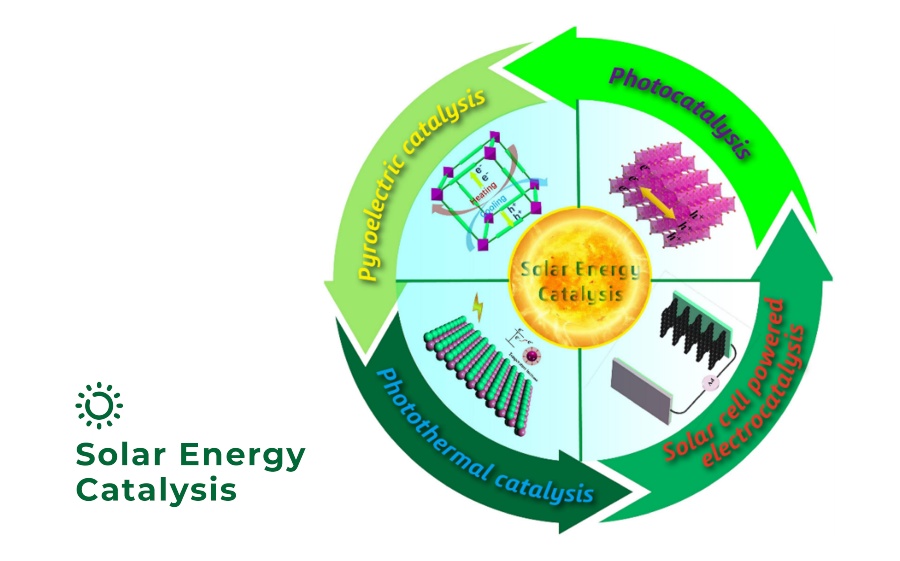
When it comes to using solar energy to promote catalytic reactions, photocatalysis technology is one of the top choices. However, sunlight can not only be directly converted into chemical energy through a photocatalytic process, it can also be converted through different energy-transfer pathways. Using sunlight as the energy source, photocatalytic reactions can proceed independently, and can also be coupled with other catalytic technologies, such as photothermal catalysis, pyroelectric catalysis, electrocatalysis and piezo-catalysis, to enhance the overall catalytic efficiency for water splitting. Therefore, Prof. Tianyi Ma’s and Prof. Baohua Jia’s group at RMIT University (Australia) recently summarized all catalytic reactions driven by sunlight without additional energy input and give them a specific definition, namely“Solar Energy Catalysis (SEC)“ (Image 1). This novel concept covers all up-to-now solar light related renewable energy conversion processes. This SEC process can utilise nothing but solar light and generate hydrogen as the final product featuring ambient condition reacion and zero emission.
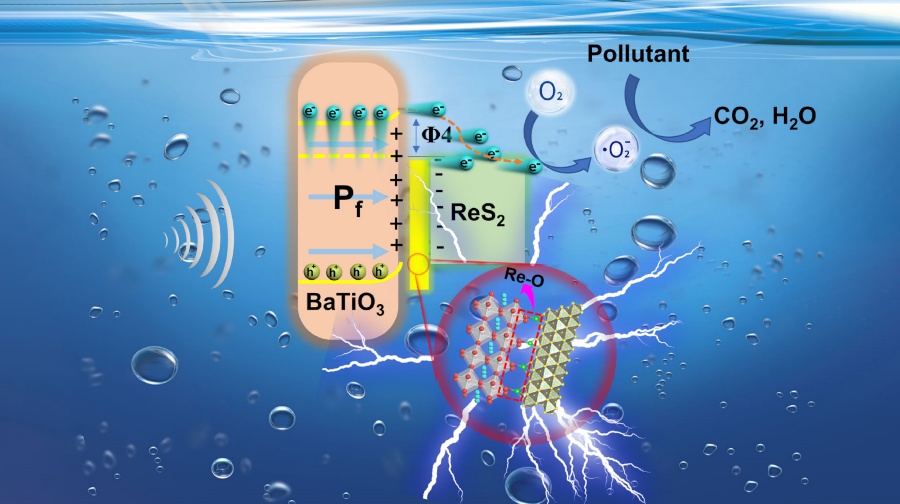
On top of this concept, they further designed the piezo-assisted photocatalysis system. Piezo-assisted photocatalysis system, as a new emerging advanced oxidation technique, can collect and utilize solar energy and natural mechanical energy (i.e., hydrodynamic energy) to realize the generation of reactive oxygen species, oxidation of water and production of hydrogen, and is considered as a promising technology to achieve environmental remediation and clean fuel generation. However, the limited reaction active sites and large electron transmission resistance severely handicap the development for its practical application. To address this issue, the group has developed multistep hydrothermal synthesis strategy to construct highly efficient and stable BaTiO3@ReS2 Schottky heterojunction, which exhibits high efficiency for photocatalysis by coupling the effect of interfacial covalent bond and piezotronics (Image 2). The internal polarization field in the Schottky interface can decrease the Schottky barrier for the migration of photogenerated charge. Therefore, the high activity as well as the excellent synergy can be obtained by BaTiO3@ReS2 system under sonication and sun light irradiation.
“It shows us the potential of using solar energy and other renewables to change our energy future. One of the key tasks is the catalytic hydrogen generation.“ said Prof. Tiany Ma. “This series of work was financially support by the veski – Study Melbourne Research Partnerships program from Victoria government, aiming to connect materials innovation community and built public’s scientific capacity via training and education, which clearly shows the determination of Australian government in the implementation of renewable energy“ said Prof. Baohua Jia.
Read the most up to date Fuel Cell and Hydrogen Industry news at FuelCellsWorks




